Neuro-Muscular Dystonia
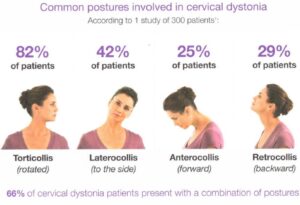 Dystonia is a movement disorder with sustained abnormal contraction of muscles resulting in an abnormal posture of the involved body parts. It can affect different parts of the body including the neck, hand, foot, and back. It may affect a group of muscles or the body.
Dystonia is a movement disorder with sustained abnormal contraction of muscles resulting in an abnormal posture of the involved body parts. It can affect different parts of the body including the neck, hand, foot, and back. It may affect a group of muscles or the body.
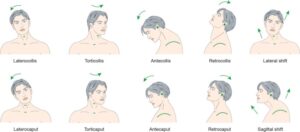
Dystonia is usually classified by the part of the body involved or the action involved: Blepharospasm (involvement of the eyelid muscles), Oromandibular dystonia (involvement of the face, jaw and/ or tongue, and combination of these, as known as oral-facial dystonia or Meige’s syndrome), Torticollis (neck), focal limb dystonia (arm or leg).
Task-specific dystonias include writer’s and musician’s cramps. These last two types of dystonia usually involve just one type of activity, while other limb activities are not involved.
As a disease, dystonia is felt to involve the basal ganglia, a part of the brain involved in the planning and execution of voluntary movements. Because the brain cells are not communicating correctly, excessive muscle contraction occurs resulting in abnormal movements. Dystonia can also be part of other diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, or as a reaction to certain medications.
 Of all movement disorders, this is one of the most prevalent, after essential tremor and Tourette’s syndrome. In North America, it is estimated that around 300,000 people of all races and ethnicities are afflicted. In most cases, normal, full life will be led. In severe cases where dystonia affects the entire body, many activities of employment and independent living are impaired.
Of all movement disorders, this is one of the most prevalent, after essential tremor and Tourette’s syndrome. In North America, it is estimated that around 300,000 people of all races and ethnicities are afflicted. In most cases, normal, full life will be led. In severe cases where dystonia affects the entire body, many activities of employment and independent living are impaired.
Medications and exercises have been used with some success to eliminate the pain and symptoms associated with dystonia.
Botox injections are of significant benefit in reducing the abnormal movements associated with many types of dystonia. While there is no cure, these treatments help to greatly improve function and comfort.
